What is smart farming?
Smart farming is the application of Internet of Things technology to traditional agriculture, using sensors and software to control agricultural production through mobile or computer platforms, making traditional agriculture more “smart”. In addition to precise perception, control, and decision-making management, in a broad sense, smart farming also includes agricultural e-commerce, food traceability and anti-counterfeiting, agricultural leisure tourism, agricultural information services, and other aspects.
“Smart agriculture” is the full application of modern information technology. Integrated application of computer and network technology, IoT technology, audio and video technology, 3S technology, wireless communication technology and expert wisdom and knowledge to realize agricultural visualized remote diagnosis, remote control, disaster warning, etc. management.
Smart farming is an advanced stage of agricultural production. It integrates emerging Internet, mobile Internet, cloud computing, and IoT technologies. It relies on various sensors (environmental temperature and humidity, soil moisture, carbon dioxide, image Etc.) and the wireless communication network to realize the intelligent perception, intelligent early warning, intelligent decision-making, intelligent analysis, expert online guidance of the agricultural production environment, and provide precise planting for agricultural production.
“Smart farming” is the comprehensive application of cloud computing, sensor networks, 3S and other information technologies in agriculture to achieve a more complete information foundation and more intimate public services. The integration of “smart farming” with modern biotechnology, planting technology and other technologies is of great significance to the construction of world-class agriculture.

What are the applications of smart farming?
Precision agriculture
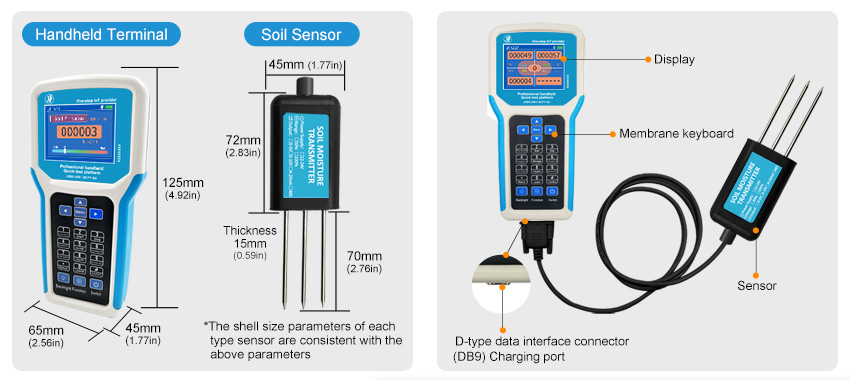
Through a large number of sensors installed in the target area of the farmland, real-time monitoring of temperature, humidity, light, gas concentration, soil moisture, electrical conductivity, and other information are summarized into the central control system. Agricultural production personnel can analyze the environment through monitoring data, thereby arranging production activities in a targeted manner, and mobilizing various execution equipment as needed, such as temperature adjustment, light adjustment, and ventilation. To realize the intelligent control of agricultural growth.
Precision Livestock Farming
Precision Livestock Farming is mainly used in the stages of breeding and disease prevention. Wearable devices (RFID ear tags) and cameras are used to collect data on livestock and poultry activities, analyze the collected data, and determine the health status, feeding status, and location of the poultry, estrus prediction. Precision Livestock Farming can effectively reduce poultry mortality and improve product quality.
Precision aquaculture
Precision aquaculture mainly refers to the installation of various sensors and monitors in aquaculture farms. The sensors can measure water quality indicators such as dissolved oxygen, pH, and temperature. The monitor can monitor the feeding, activity, or death of the fish. These analog signals are finally converted into digital signals. The terminal equipment expresses the digital signals in text or graphic format so that the water quality can be monitored in real-time and detailed charts can be drawn. Through long-term continuous monitoring, adjustment and control of water quality, the breeding objects are placed in the most suitable environment for growth. Achieve the effect of increasing production, saving energy, and reducing the labor intensity of workers. In this way, resources are saved, waste is avoided, breeding risks are reduced, and breeding benefits are improved.

Smart greenhouse
Smart greenhouse usually refers to the multi-span greenhouse or modern greenhouse. It is an advanced type in facility agriculture and has a comprehensive environmental control system. The system can directly adjust the indoor temperature, light, water, fertilizer, gas, and many other factors. It can achieve high production throughout the year and good economic benefits. In recent years, with the rapid development of vegetable greenhouse construction, smart greenhouses have brought impetus to agricultural development.
How is the development of global smart farming?
From a global perspective, the United States is a typical representative of the operation of smart farming. The agricultural aviation application technology in the United States is relatively mature, and a relatively complete agricultural aviation industry system has been formed. Statistics show that the direct contribution rate of American Agricultural Aviation to agriculture is more than 15%.
Germany has invested a lot of money in the development of agricultural technology, and large companies have led the development of “digital agriculture” technology. The work of modern German farmers is inseparable from the support of computers and the Internet. The job at the beginning of every morning is to check the weather information of the day, check the market price of food and check emails.
Besides, in rice production in Japan, the amount of micro-agricultural drones has exceeded that of manned helicopters. The use of micro-agricultural drones for agricultural production has become one of the important trends in Japan’s agricultural development. In Canada, smart farming also incorporates agricultural Internet of Things information technology.
Australia established the National Livestock Identification Scheme (NLIS) more than ten years ago, that is, the quality and safety traceability system of livestock products. The rumen marking ball or ear tag certified by NLIS is used to identify cattle and sheep. The national central database records the identity of cattle and sheep. The unified management of information can track the entire process of individual animals from birth to slaughter. The Netherlands government vigorously develops satellite + big data to realize smart precision farming.
The agricultural big data website created by France brings more opportunities to farmers and changes the relationship between farmers and stakeholders such as banks, insurance companies, and agricultural mutual cooperatives.
Israel’s agriculture has high information and digital foundation. Many agricultural technology innovation companies use big data to help Israeli farmers and provide more personalized farming solutions based on the specific conditions of different farms.
The development of smart farming and the IoT has promoted the third green revolution in the world. Based on more precise and resource-efficient methods, smart farming has the real potential to provide more productive and sustainable forms of agricultural production.