A met station is a vital tool for monitoring and predicting weather patterns. It is an instrument monitor atmospheric conditions such as temperature, humidity, wind speed and direction, air pressure. The data collected from weather stations is used for various purposes such as weather forecasting, aviation, agriculture, and research.
Understand met stations

met stations have come a long way from the traditional mercury thermometers and barometers. Today, they carry with them advanced sensors and technologies that allow them to collect accurate and precise data. In this article, we will explore the various components of a weather station, their functions, and the applications of weather stations.
Components of a Weather Station
Met stations comprises several components that work together to measure and record atmospheric conditions. These components include:
Thermometer:
A thermometer is an instrument measure temperature. In a weather station, thermometers are used to measure air temperature and soil temperature.
Hygrometer:
A hygrometer is an instrument measure humidity. In a weather station, hygrometers are used to measure relative humidity and dew point.
Barometer:
A barometer is an instrument measure air pressure. In a weather station, barometers are used to measure atmospheric pressure and provide information on changes in weather patterns.
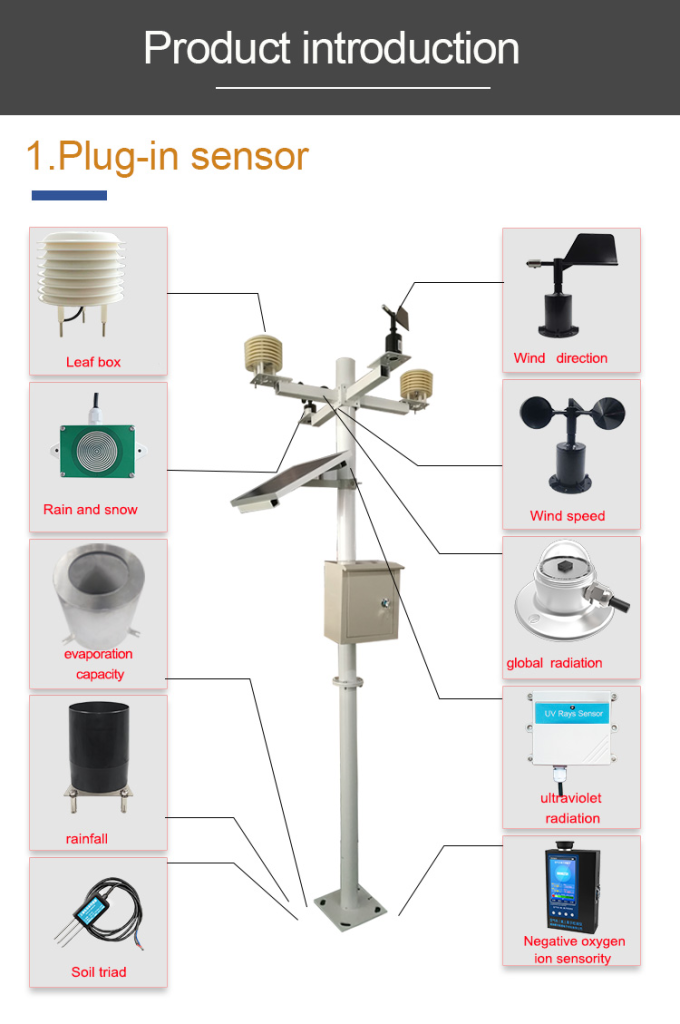
Anemometer:
An anemometer is an instrument measure wind speed. In a weather station, anemometers are used to measure wind speed and direction.
Rain Gauge:
A rain gauge is an instrument monitor precipitation. In a weather station, rain gauges are used to measure rainfall and snowfall.
Weather Vane:
A weather vane is an instrument monitor wind direction. In a weather station, weather vanes are used to determine the direction of the wind.
Solar Radiation Sensor:
A solar radiation sensor is an instrument measure the amount of solar radiation received at a particular location. In a weather station, solar radiation sensors are used to measure the amount of solar radiation received on the earth’s surface.
Data Logger:
A data logger is an instrument record and store data collected by the various sensors in a weather station. Data loggers are used to store data for later analysis and to transmit data to a central location.
Functions of a Weather Station
The primary function of a met station is to collect and record data on atmospheric conditions. The data collected is used for various purposes such as weather forecasting, aviation, agriculture, and research. The functions of a weather station include:

Weather Forecasting: Weather stations are used to collect data on atmospheric conditions, which is used to generate weather forecasts. Weather forecasts are essential for planning outdoor activities, agriculture, aviation, and other industries that are dependent on weather conditions.
Aviation:
Weather stations are used in aviation to provide pilots with information on weather conditions such as wind speed and direction, temperature, and air pressure. This information is critical for safe and efficient flight operations.
Agriculture:
Weather stations are used in agriculture to provide farmers with information on weather conditions such as temperature, humidity, and precipitation. This information is used to make decisions on planting, irrigation, and harvesting.
Research:
Weather stations are used in research to collect data on atmospheric conditions for scientific studies and experiments. This data is used to study climate change, weather patterns, and other atmospheric phenomena.
Applications of Weather Stations
Met stations have various applications in different industries. Some of the applications of weather stations include:
Agriculture:
Weather stations are used in agriculture to provide farmers with information on weather conditions such as temperature, humidity, and precipitation. This information is used to make decisions on planting, irrigation, and harvesting.

Aviation:
Weather stations are used in aviation to provide pilots with information on weather conditions such as wind speed and direction, temperature, and air pressure. This information is critical for safe and efficient flight operations.
Energy:
Weather stations are used in the energy industry to provide information on wind speed and direction, temperature, and solar radiation. This information is used to optimize the production of renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power.
Construction:
Weather stations are used in construction to provide information on weather conditions such as temperature, humidity, and precipitation. This information is used to plan construction schedules and ensure worker safety.
Transportation:
People also use weather stations for transportation to provide information about weather conditions.
Challenges and Future Developments
Despite the advancements in weather station technology, there are still challenges that need to be addressed. Some of the challenges include:
Data Quality:

The accuracy and precision of data collected by weather stations are critical for weather forecasting and other applications. Ensuring data quality is essential for reliable and accurate weather predictions.
Maintenance:
Weather stations require regular maintenance to ensure that they continue to function correctly. Regular maintenance is essential for the longevity of weather stations and the accuracy of data collected.
Data Accessibility:
The accessibility of weather station data is critical for weather forecasting and other applications. Ensuring that data is accessible to the public and other stakeholders is essential for effective decision-making.
Integration with other Technologies:
The integration of weather station data with other technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning holds immense potential for improving weather forecasting and other applications.
Conclusion
Weather stations are vital tools for monitoring and predicting weather patterns. They comprise several components that work together to measure and record atmospheric conditions. The data collected from weather stations is used for various purposes such as weather forecasting, aviation, agriculture, and research. Despite the challenges, weather station technology continues to evolve, and the integration of weather station data with other technologies holds immense potential for improving weather forecasting and other applications. With ongoing innovation and adoption, weather stations are poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of weather forecasting and other industries that are dependent on weather conditions.
