Introduction to weather sensors
Our weather sensors provide accurate and reliable weather data for a wide range of applications. With advanced iot sensors and wireless connectivity, it provides the necessary information for weather forecasting, agricultural planning, outdoor safety, and research. Keep in touch with the weather station.

Accurate weather forecasting plays a crucial role in various aspects of our lives, ranging from planning outdoor activities to making informed decisions in agriculture, transportation, and disaster management. In order to obtain precise weather predictions, meteorologists heavily rely on a range of essential weather sensors. These instruments enable the collection of accurate data, which is then analyzed to make reliable forecasts. In this article, we will explore some of the key weather instruments that are essential for accurate weather forecasting.
The variety of key weather instruments
- Temperature and humidity sensor
- Atmospheric pressure sensor
- Wind speed sensor
- Rain Gauge:
- Rain and snow sensor
- Photosynthetically active radiation sensor
Temperature and humidity sensor

The temperature and humidity sensor is a fundamental instrument used to measure temperature. It provides vital information about atmospheric conditions, which helps in identifying weather patterns and trends. Modern thermometers come in various forms, including digital and mercury-based ones, and are designed for both indoor and outdoor use. By monitoring temperature changes, meteorologists can assess the possibility of heatwaves, cold fronts, or other temperature-related phenomena.
Atmospheric pressure sensor
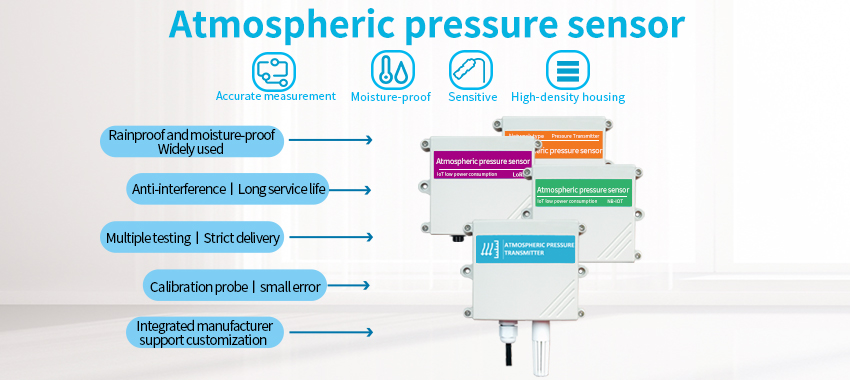
A atmospheric pressure sensor is used to measure atmospheric pressure. It helps in predicting short-term weather changes such as approaching storms or clearing skies. Decreasing atmospheric pressure often indicates the possibility of deteriorating weather conditions, while rising pressure signals fair weather. The barometer assists meteorologists in understanding the movement of air masses and forecasting weather patterns accurately.
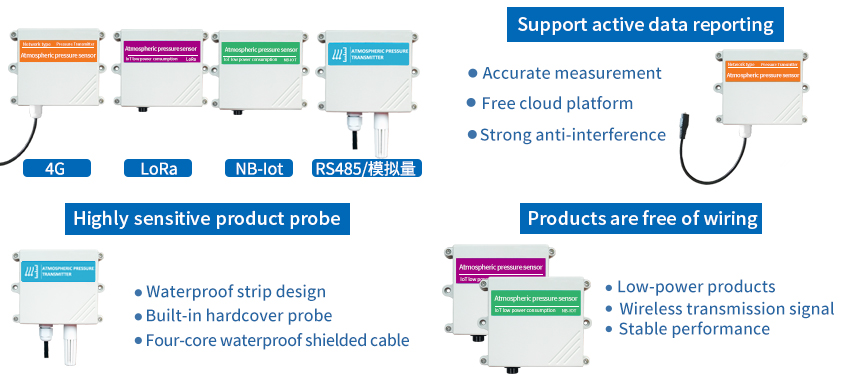
Parameters:
Measurement parameter: atmospheric pressure
Model Number: JXBS-3001-QY-V10-1
Communication mode: 0-10V
Power supply: 12-24V power supply
Measurement range: 10-1200mbar
Material: ABS.
Maximum power: <4W
Accuracy: + / – 1.5 mbar
Working range: 0-40℃/0-80RH%
Power consumption: 0.15 W or less
Air pressure transmitter can accurately measure atmospheric pressure value, suitable for pressure measurement under various circumstances. Adopt imported sensors, measurement data is stable, high precision, strong anti-interference ability, long service life and can be widely applied to computer room environment, airports, railway stations, commercial buildings, family homes, office buildings, schools, meeting rooms, shopping malls, restaurants, the gym, cinema, library, etc, it has broad application prospects.
Wind speed sensor:

The wind speed sensor measures wind speed and direction. It is a critical instrument for assessing the impact of wind on weather conditions. By analyzing wind patterns, meteorologists can predict the movement of weather systems, determine the strength of storms, and issue relevant warnings. Anemometers are commonly deployed in weather stations, airports, and offshore locations.

Parameters:
Material: Aluminum alloy
Suitable for: wind speed sensor/weather station
Wind speed measurement range: 0-30m/s
Wind speed measurement accuracy: ±1m/s
Response time: less than 5 seconds
Power supply: 12V to 24V DC
Power consumption: < 1 w
Operating temperature: -30-80℃
Modern wind speed sensor employ advanced technologies such as ultrasonic or laser to offer more precise and stable wind speed measurements. These sensors are widely used in meteorological monitoring, aviation, energy production, and building design. By accurately measuring wind speed, they enable better understanding and prediction of weather conditions, as well as the implementation of appropriate measures to ensure safety and enhance efficiency.
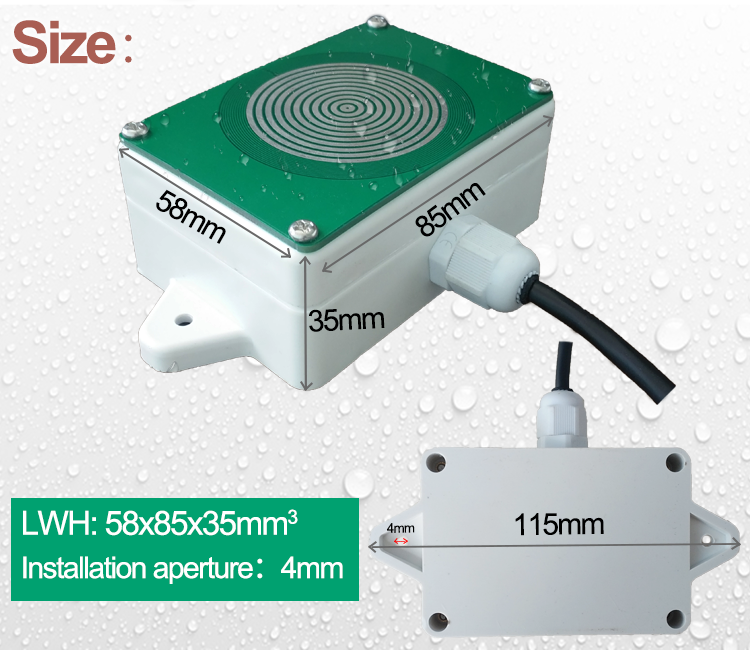
Rain Gauge:

A rain gauge is a device used to measure the amount of rainfall in a particular area. It consists of a cylindrical container with a calibrated scale, allowing for accurate measurement of precipitation. When rain falls into the gauge, the water level rises and provides a visual indication of the rainfall amount. Some modern rain gauges may also include electronic sensors for automated data collection.
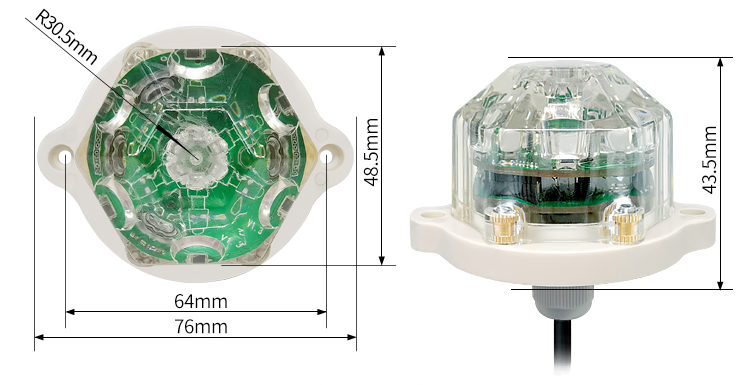
Parameters:
Measurement parameter: rainfall
Output mode: RS485 output
Power supply: 12V to 24V DC
Power consumption: ≤0.2W (12V DC, 25℃)
Operating temperature: -30℃ to +50℃
Operating humidity environment: 0%-99%RH (relative humidity), non-condensing
Working pressure range: standard atmospheric pressure ± 10%
Overall dimension: 75.94*64*45.5mm (length * width * height)
For accurate precipitation measurement, meteorologists use rain gauges. These weather instruments collect and measure the amount of rainfall over a specific area within a specific time frame. Precipitation data is essential for climate studies, flood forecasting, and agricultural planning. Rain gauges come in different forms, but the most common type is a cylindrical container with marked levels to measure the depth of collected rainwater.
Rain and snow sensor

A rain and snow sensor is a qualitative measurement device used to measure whether it is raining or snowing outdoors or in nature. It has high sensitivity and internal automatic heating mode, which can effectively prevent measurement errors caused by icing on the sensor surface in cold weather.

Parameters:
Communication method: 4g
Power supply: 12-24V power supply
Measuring range: Without
Material: ABS.
Detection object: rain, snow and other precipitation weather
Type of switching quantity: normally open contact
Power consumption: ≤0.15W (@12V DC, 25℃) /≤2.5W (@ heating state)
Working environment: -20℃-60℃ 0-95%RH
Operating power: 120VAC/24VDC
Heating function opening temperature: 10℃
Rain and snow sensor monitoring data is critical for weather monitoring, flood prediction and water resource management. By accurately measuring and distinguishing different forms of precipitation, these sensors contribute to enhancing our understanding of weather patterns and improving decision-making in various industries and sectors.
Photosynthetically active radiation sensor
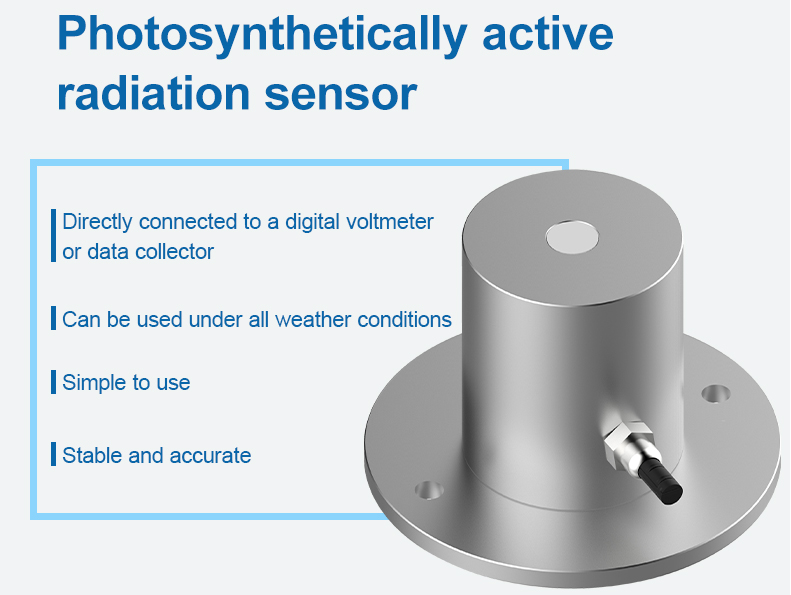
PAR sensor, also known as light quantum number, is mainly measure the photosynthetically active radiation of natural light in the wavelength range of 400 ~ 700nm. It is simple to use and can be directly connected to a digital voltmeter or data collector. It can be used in all-weather conditions.
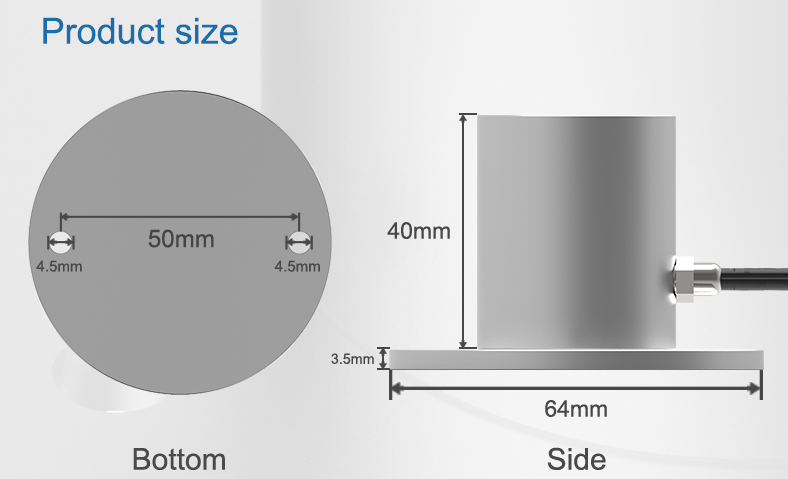
PAR sensor capture light energy and convert it into electrical signals to determine the plant’s photosynthetic activity. These sensors play a vital role in agricultural and horticultural applications, enabling farmers and researchers to optimize crop growth and productivity by monitoring and adjusting light levels.
The advantages of important weather instruments

- Weather Monitoring: Our weather station is equipped with sensors that measure temperature, humidity, wind speed, wind direction, barometric pressure, and rainfall. By continuously monitoring these parameters, it provides real-time data on weather conditions.
- Accuracy and Reliability: Our weather station is designed to deliver precise and reliable weather data. The sensors are calibrated to ensure accurate measurements, and the device operates with high data resolution to capture even slight variations in weather patterns.
- Data Display and Analysis: The weather station features a user-friendly interface that displays the collected data in an intuitive format. Users can easily navigate through various weather parameters and analyze the data to understand weather patterns and trends.
- Customizable Alerts: The weather station can be programmed to send alerts based on predefined thresholds. Users can set up notifications for specific weather conditions such as high winds, heavy rainfall, or extreme temperatures, enhancing safety and preparedness.
- Wireless Connectivity: Our weather station is equipped with wireless capabilities, allowing users to connect it to their smartphones or computers. The data can be accessed remotely, enabling users to monitor weather conditions from anywhere and share the data with others.
Conclusion:
To ensure accurate and reliable weather forecasting, meteorologists rely on a range of essential weather instruments. Thermometers, barometers, hygrometers, anemometers, and rain gauges are just a few examples of the instruments that enable the collection of critical atmospheric data. By using these instruments and analyzing the gathered information, meteorologists can make informed predictions about weather conditions, helping individuals and organizations make well-informed decisions in various fields. With advancements in technology, these weather instruments continue to evolve, providing even greater precision and contributing to improving weather forecasts around the world.
