In the realm of modern agriculture, the efficient use of water resources is paramount to ensuring sustainable crop production and environmental stewardship. Irrigation scheduling plays a crucial role in optimizing water usage and maximizing crop yields, and soil moisture sensors have emerged as indispensable tools in this endeavor. By providing real-time data on soil moisture levels, these sensors enable farmers to make informed decisions about when and how much to irrigate, leading to improved water management practices, enhanced crop quality, and increased productivity.

Understanding the Importance of Soil Moisture Sensor
Soil moisture sensors are instrumental in monitoring the water content in the soil, which is vital for determining the water needs of crops. These sensors come in various types, including capacitance sensors, tensiometers, and neutron probes, each offering unique advantages in terms of accuracy, precision, and ease of use. By strategically placing soil moisture sensor in the field, farmers can gather valuable data on soil moisture levels at different depths and locations, allowing for site-specific irrigation decisions tailored to the specific needs of the crops.
Benefits of Using Soil Moisture Sensor
The utilization of soil moisture sensor for irrigation scheduling offers a plethora of benefits for farmers and the environment. By accurately measuring soil moisture levels, farmers can avoid over-irrigation, which not only wastes water but can also lead to nutrient leaching and soil erosion. Conversely, under-irrigation can result in crop stress and reduced yields. Soil moisture sensor enable precise irrigation scheduling based on real-time data, ensuring that crops receive the optimal amount of water needed for healthy growth and development.
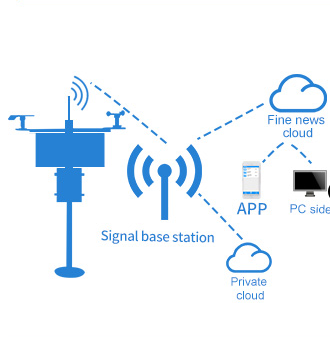
Moreover, the use of soil moisture sensor can help farmers save on water and energy costs associated with irrigation. By avoiding unnecessary irrigation cycles and ensuring that water is applied only when needed, farmers can reduce water wastage and energy consumption, leading to cost savings and improved operational efficiency. Additionally, by promoting water conservation and sustainable irrigation practices, soil moisture sensor contribute to environmental sustainability and the preservation of water resources for future generations.
Best Practices for Soil Moisture Sensors
To maximize the benefits of soil moisture sensor for irrigation scheduling, farmers should adhere to best practices in sensor placement, calibration, and data interpretation. Proper placement of sensors at representative locations within the field is crucial for obtaining accurate and reliable data on soil moisture levels. Calibration of sensors using known standards and regular maintenance checks are essential to ensure the accuracy of measurements and optimize sensor performance over time.

Furthermore, farmers should develop irrigation schedules based on the data provided by soil moisture sensors, taking into account factors such as crop water requirements, soil type, weather conditions, and irrigation system efficiency. By integrating soil moisture sensor data with weather forecasts and crop evapotranspiration rates, farmers can fine-tune their irrigation schedules to meet the specific needs of their crops while minimizing water waste and maximizing water use efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, soil moisture sensor are invaluable tools for enhancing agricultural efficiency and sustainability through optimized irrigation scheduling. By providing real-time data on soil moisture levels, these sensors enable farmers to make informed decisions about irrigation timing and volume, leading to improved water management practices, increased crop yields, and cost savings. As the importance of water conservation and sustainable agriculture continues to grow, the adoption of soil moisture sensor in irrigation management will play a crucial role in ensuring the long-term viability of agricultural operations and the preservation of water resources for future generations.
